This is the multi-page printable view of this section.
Click here to print.
Return to the regular view of this page.
ADOT Configuration
OpenTelemetry Collector provides a vendor-agnostic solution to receive, process and export telemetry data. It removes the need to run, operate, and maintain multiple agents/collectors. ADOT Collector is an AWS-supported distribution of the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command kubectl apply -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for ADOT
1 - ADOT with AMP and AMG
This tutorial demonstrates how to config the ADOT package to scrape metrics from an EKS Anywhere cluster, and send them to Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus
(AMP) and Amazon Managed Grafana
(AMG).
This tutorial walks through the following procedures:
Note
- We included
Test sections below for critical steps to help users to validate they have completed such procedure properly. We recommend going through them in sequence as checkpoints of the progress.
- We recommend creating all resources in the
us-west-2 region.
Create an AMP workspace
An AMP workspace is created to receive metrics from the ADOT package, and respond to query requests from AMG. Follow steps below to complete the set up:
-
Open the AMP console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/prometheus/.
-
Choose region us-west-2 from the top right corner.
-
Click on Create to create a workspace.
-
Type a workspace alias (adot-amp-test as an example), and click on Create workspace.
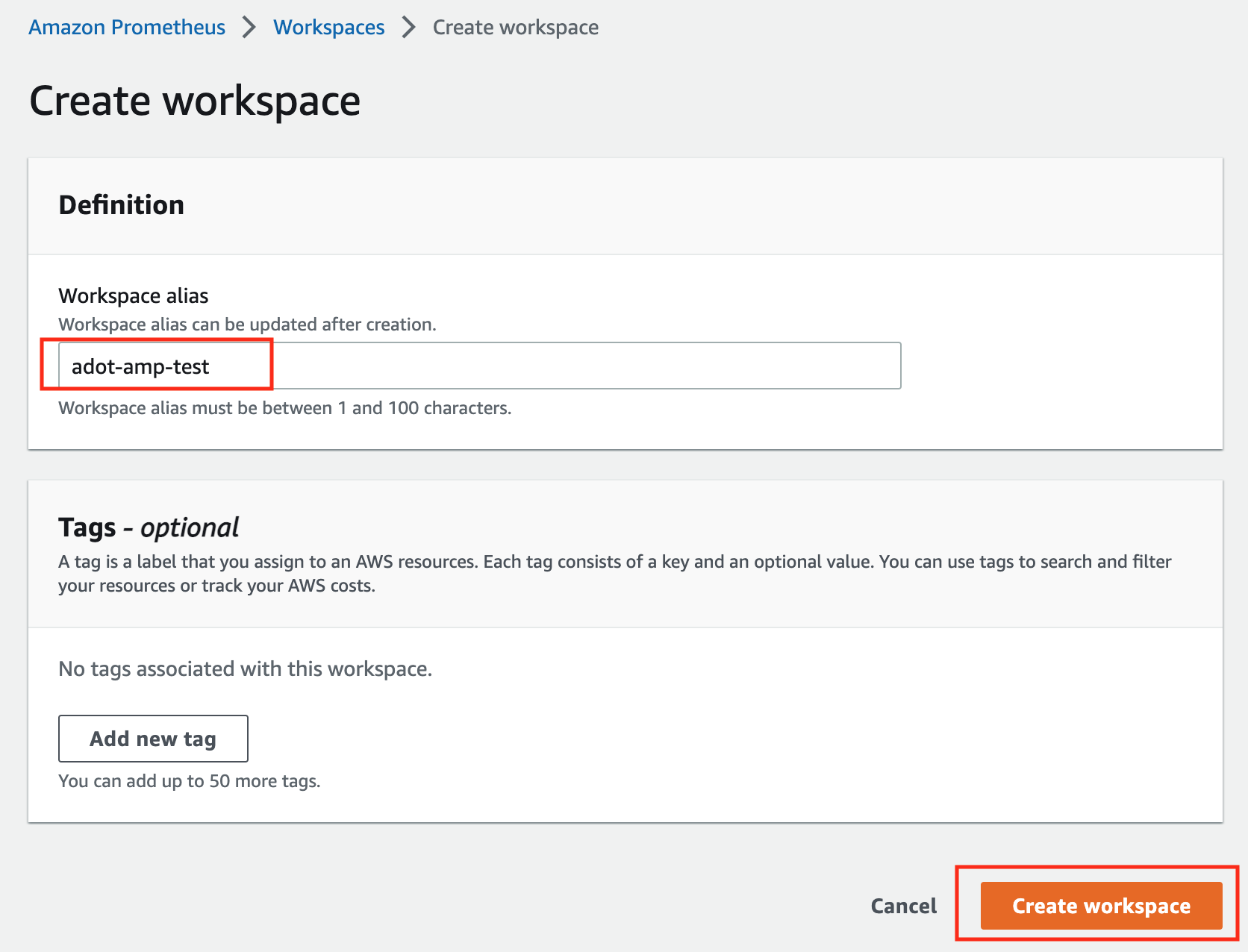
-
Make notes of the URLs displayed for Endpoint - remote write URL and Endpoint - query URL. You’ll need them when you configure your ADOT package to remote write metrics to this workspace and when you query metrics from this workspace. Make sure the workspace’s Status shows Active before proceeding to the next step.
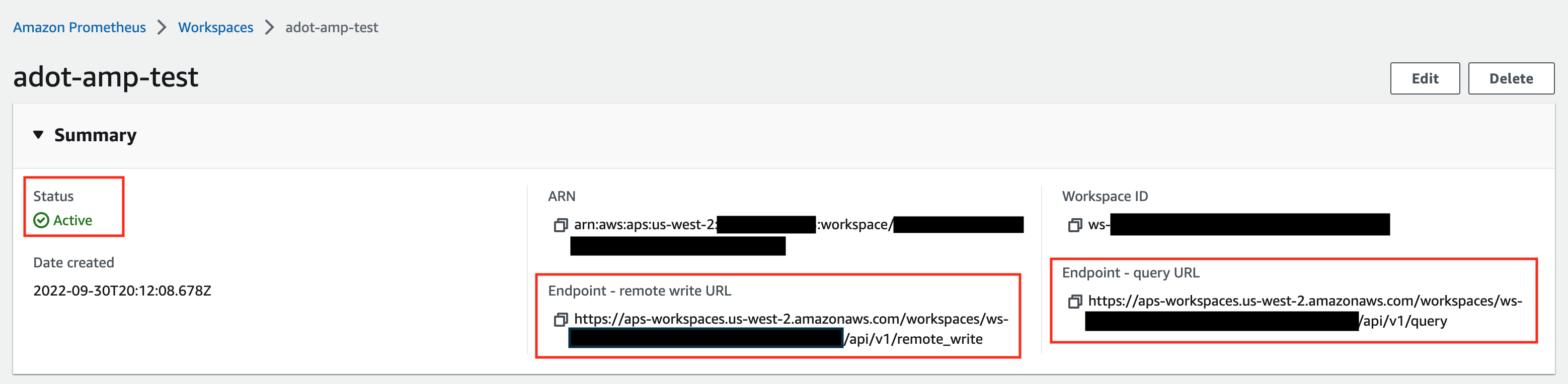
For additional options (i.e. through CLI) and configurations (i.e. add a tag) to create an AMP workspace, refer to AWS AMP create a workspace guide.
Create a cluster with IRSA
To enable ADOT pods that run in EKS Anywhere clusters to authenticate with AWS services, a user needs to set up IRSA at cluster creation. EKS Anywhere cluster spec for Pod IAM
gives step-by-step guidance on how to do so. There are a few things to keep in mind while working through the guide:
-
While completing step Create an OIDC provider
, a user should:
-
create the S3 bucket in the us-west-2 region, and
-
attach an IAM policy with proper AMP access to the IAM role.
Below is an example that gives full access to AMP actions and resources. Refer to AMP IAM permissions and policies guide
for more customized options.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"aps:*"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
-
While completing step deploy pod identity webhook
, a user should:
- make sure the service account is created in the same namespace as the ADOT package (which is controlled by the
package definition file with field spec.targetNamespace);
- take a note of the service account that gets created in this step as it will be used in ADOT package installation;
- add an annotation
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: <role-arn> to the created service account.
By default, the service account is installed in the default namespace with name pod-identity-webhook, and the annotation eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: <role-arn> is not added automatically.
IRSA Set Up Test
To ensure IRSA is set up properly in the cluster, a user can create an awscli pod for testing.
-
Apply the following yaml file in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: awscli
spec:
serviceAccountName: pod-identity-webhook
containers:
- image: amazon/aws-cli
command:
- sleep
- "infinity"
name: awscli
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
EOF
-
Exec into the pod:
kubectl exec -it awscli -- /bin/bash
-
Check if the pod can list AMP workspaces:
aws amp list-workspaces --region=us-west-2
-
If the pod has issues listing AMP workspaces, re-visit IRSA set up guidance before proceeding to the next step.
-
Exit the pod:
exit
Install the ADOT package
The ADOT package will be created with three components:
-
the Prometheus Receiver, which is designed to be a drop-in replacement for a Prometheus Server and is capable of scraping metrics from microservices instrumented with the Prometheus client library
;
-
the Prometheus Remote Write Exporter, which employs the remote write features and send metrics to AMP for long term storage;
-
the Sigv4 Authentication Extension, which enables ADOT pods to authenticate to AWS services.
Follow steps below to complete the ADOT package installation:
-
Update the following config file. Review comments carefully and replace everything that is wrapped with a <> tag. Note this configuration aims to mimic the Prometheus community helm chart. A user can tailor the scrape targets further by modifying the receiver section below. Refer to ADOT package spec
for additional explanations of each section.
Click to expand ADOT package config
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: default # this needs to match the namespace of the serviceAccount below
config: |
mode: deployment
serviceAccount:
# Specifies whether a service account should be created
create: false
# Annotations to add to the service account
annotations: {}
# Specifies the serviceAccount annotated with eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn.
name: "pod-identity-webhook" # name of the service account created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
config:
extensions:
sigv4auth:
region: "us-west-2"
service: "aps"
assume_role:
sts_region: "us-west-2"
receivers:
# Scrape configuration for the Prometheus Receiver
prometheus:
config:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: kubernetes-apiservers
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
- __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
- job_name: kubernetes-nodes
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
target_label: __address__
- regex: (.+)
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$$1/proxy/metrics
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_node_name
target_label: __metrics_path__
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
- job_name: kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
target_label: __address__
- regex: (.+)
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_node_name
target_label: __metrics_path__
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
- job_name: kubernetes-service-endpoints
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
target_label: kubernetes_name
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name
target_label: kubernetes_node
- job_name: kubernetes-service-endpoints-slow
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape_slow
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
target_label: kubernetes_name
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name
target_label: kubernetes_node
scrape_interval: 5m
scrape_timeout: 30s
- job_name: prometheus-pushgateway
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: pushgateway
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe
- job_name: kubernetes-services
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module:
- http_2xx
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe
- source_labels:
- __address__
target_label: __param_target
- replacement: blackbox
target_label: __address__
- source_labels:
- __param_target
target_label: instance
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
target_label: kubernetes_name
- job_name: kubernetes-pods
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_name
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
- action: drop
regex: Pending|Succeeded|Failed|Completed
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_phase
- job_name: kubernetes-pods-slow
scrape_interval: 5m
scrape_timeout: 30s
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape_slow
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_name
target_label: pod
- action: drop
regex: Pending|Succeeded|Failed|Completed
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_phase
processors:
batch/metrics:
timeout: 60s
exporters:
logging:
logLevel: info
prometheusremotewrite:
endpoint: "<AMP-WORKSPACE>/api/v1/remote_write" # Replace with your AMP workspace
auth:
authenticator: sigv4auth
service:
extensions:
- health_check
- memory_ballast
- sigv4auth
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [prometheus]
processors: [batch/metrics]
exporters: [logging, prometheusremotewrite]
-
Bind additional roles to the service account pod-identity-webhook (created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
) by applying the following file in the cluster (using kubectl apply -f <file-name>). This is because pod-identity-webhook by design does not have sufficient permissions to scrape all Kubernetes targets listed in the ADOT config file above. If modifications are made to the Prometheus Receiver, make updates to the file below to add / remove additional permissions before applying the file.
Click to expand clusterrole and clusterrolebinding config
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: otel-prometheus-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
- nodes/proxy
- services
- endpoints
- pods
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- nonResourceURLs:
- /metrics
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: otel-prometheus-role-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: otel-prometheus-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: pod-identity-webhook # replace with name of the service account created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
namespace: default # replace with namespace where the service account was created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
-
Use the ADOT package config file defined above to complete the ADOT installation. Refer to ADOT installation guide
for details.
ADOT Package Test
To ensure the ADOT package is installed correctly in the cluster, a user can perform the following tests.
Check pod logs
Check ADOT pod logs using kubectl logs <adot-pod-name> -n <namespace>. It should display logs similar to below.
...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.184Z info service/telemetry.go:103 Setting up own telemetry...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.184Z info service/telemetry.go:138 Serving Prometheus metrics {"address": "0.0.0.0:8888", "level": "basic"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.185Z info components/components.go:30 In development component. May change in the future. {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "logging", "stability": "in development"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:42 Starting extensions...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:45 Extension is starting... {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info healthcheckextension@v0.58.0/healthcheckextension.go:44 Starting health_check extension {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check", "config": {"Endpoint":"0.0.0.0:13133","TLSSetting":null,"CORS":null,"Auth":null,"MaxRequestBodySize":0,"IncludeMetadata":false,"Path":"/","CheckCollectorPipeline":{"Enabled":false,"Interval":"5m","ExporterFailureThreshold":5}}}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:49 Extension started. {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:45 Extension is starting... {"kind": "extension", "name": "memory_ballast"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info ballastextension/memory_ballast.go:52 Setting memory ballast {"kind": "extension", "name": "memory_ballast", "MiBs": 0}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info extensions/extensions.go:49 Extension started. {"kind": "extension", "name": "memory_ballast"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info extensions/extensions.go:45 Extension is starting... {"kind": "extension", "name": "sigv4auth"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info extensions/extensions.go:49 Extension started. {"kind": "extension", "name": "sigv4auth"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:74 Starting exporters...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:78 Exporter is starting... {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "logging"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:82 Exporter started. {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "logging"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:78 Exporter is starting... {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "prometheusremotewrite"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:82 Exporter started. {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "prometheusremotewrite"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:86 Starting processors...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:90 Processor is starting... {"kind": "processor", "name": "batch/metrics", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:94 Processor started. {"kind": "processor", "name": "batch/metrics", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:98 Starting receivers...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:102 Receiver is starting... {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.188Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.188Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.188Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:106 Receiver started. {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info healthcheck/handler.go:129 Health Check state change {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check", "status": "ready"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info service/collector.go:215 Starting aws-otel-collector... {"Version": "v0.21.1", "NumCPU": 2}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info service/collector.go:128 Everything is ready. Begin running and processing data.
...
Check AMP endpoint using awscurl
Use awscurl commands below to check if AMP received the metrics data sent by ADOT. The awscurl tool is a curl like tool with AWS Signature Version 4 request signing. The command below should return a status code success.
pip install awscurl
awscurl -X POST --region us-west-2 --service aps "<amp-query-endpoint>?query=up"
Create an AMG workspace and connect to the AMP workspace
An AMG workspace is created to query metrics from the AMP workspace and visualize the metrics in user-selected or user-built dashboards.
Follow steps below to create the AMG workspace:
-
Enable AWS Single-Sign-on (AWS SSO). Refer to IAM Identity Center
for details.
-
Open the Amazon Managed Grafana console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/grafana/.
-
Choose Create workspace.
-
In the Workspace details window, for Workspace name, enter a name for the workspace.
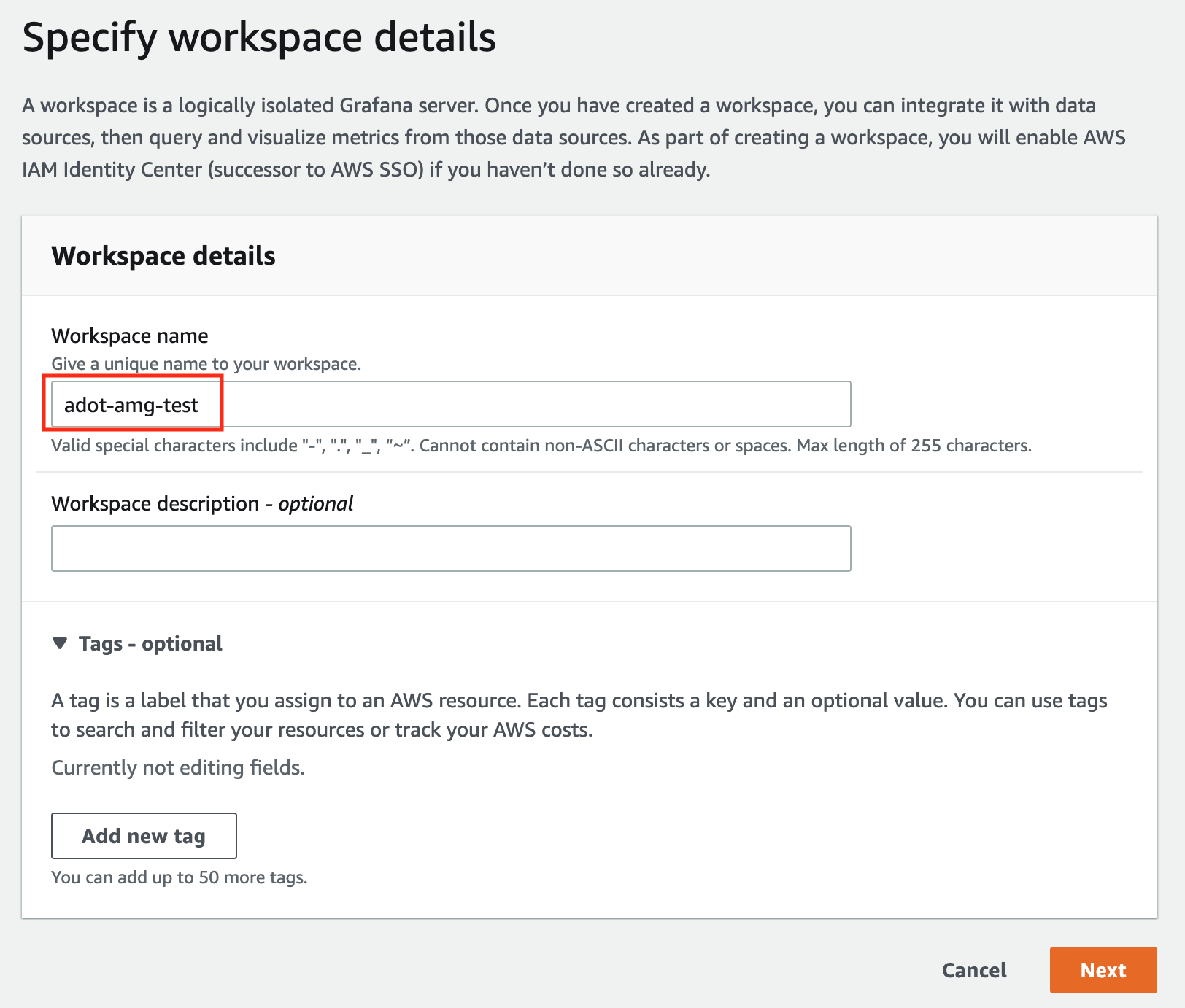
-
In the config settings window, choose Authentication access by AWS IAM Identity Center, and Permission type of Service managed.
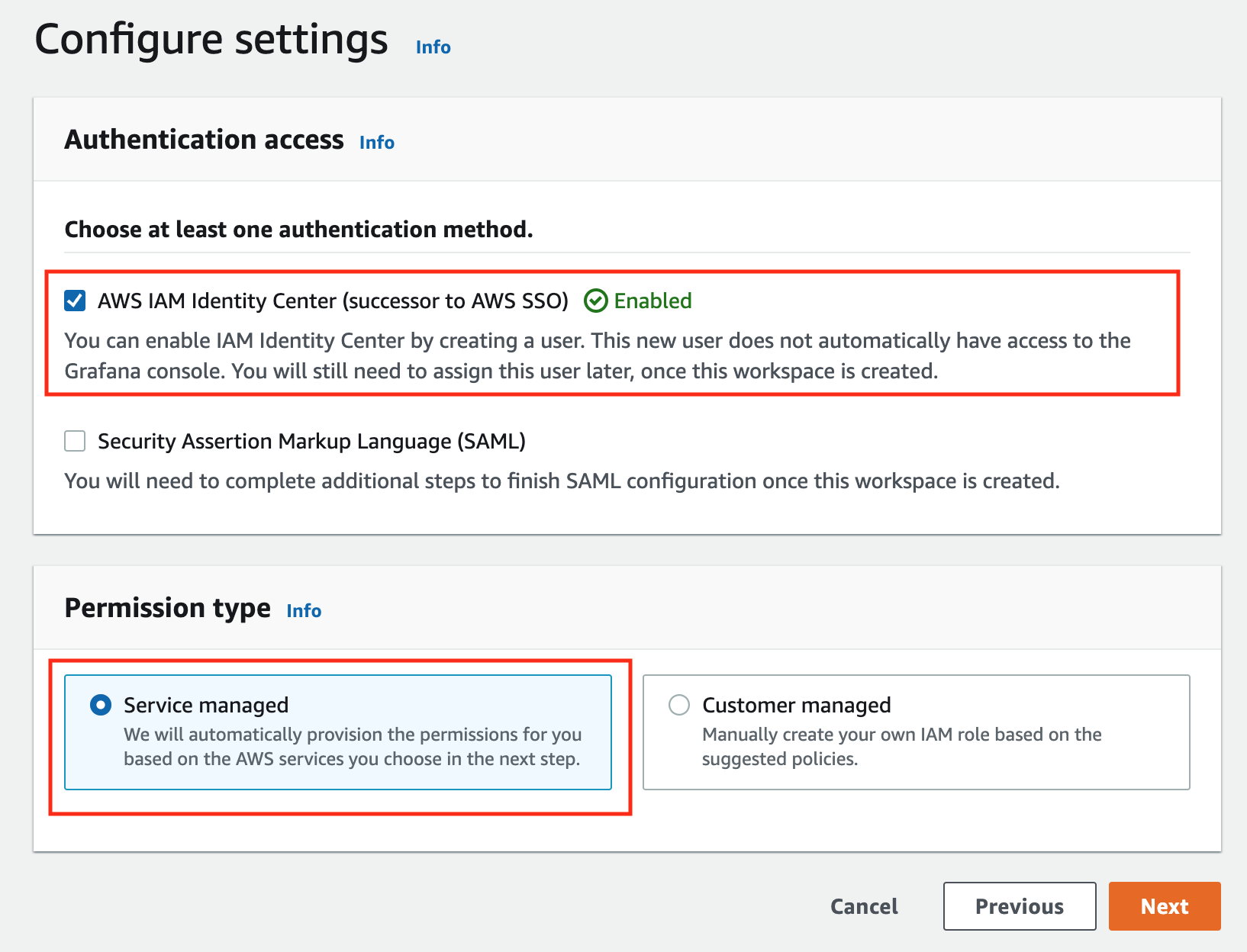
-
In the IAM permission access setting window, choose Current account access, and Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus as data source.
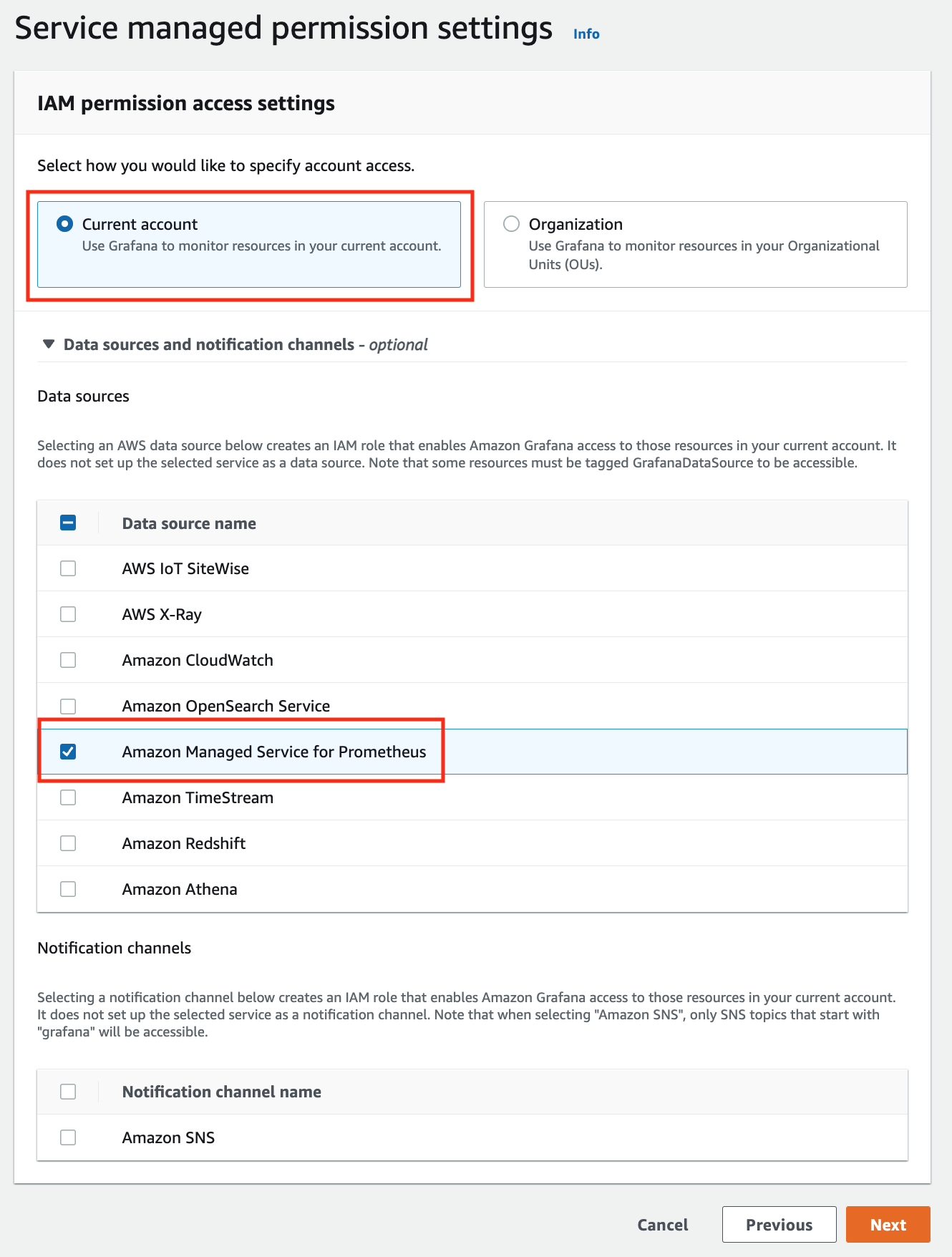
-
Review all settings and click on Create workspace.
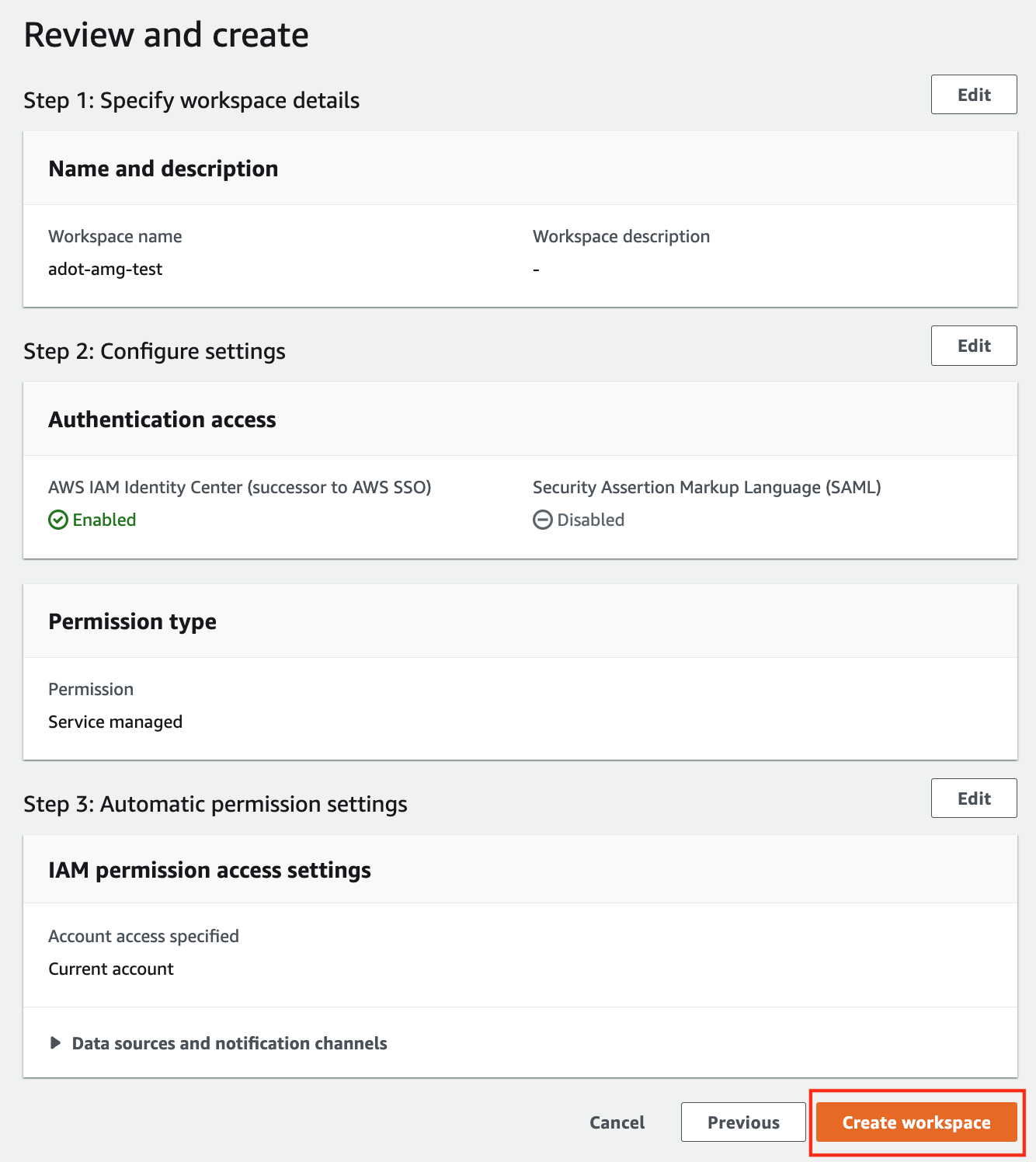
-
Once the workspace shows a Status of Active, you can access it by clicking the Grafana workspace URL. Click on Sign in with AWS IAM Identity Center to finish the authentication.
Follow steps below to add the AMP workspace to AMG.
-
Click on the config sign on the left navigation bar, select Data sources, then choose Prometheus as the Data source.
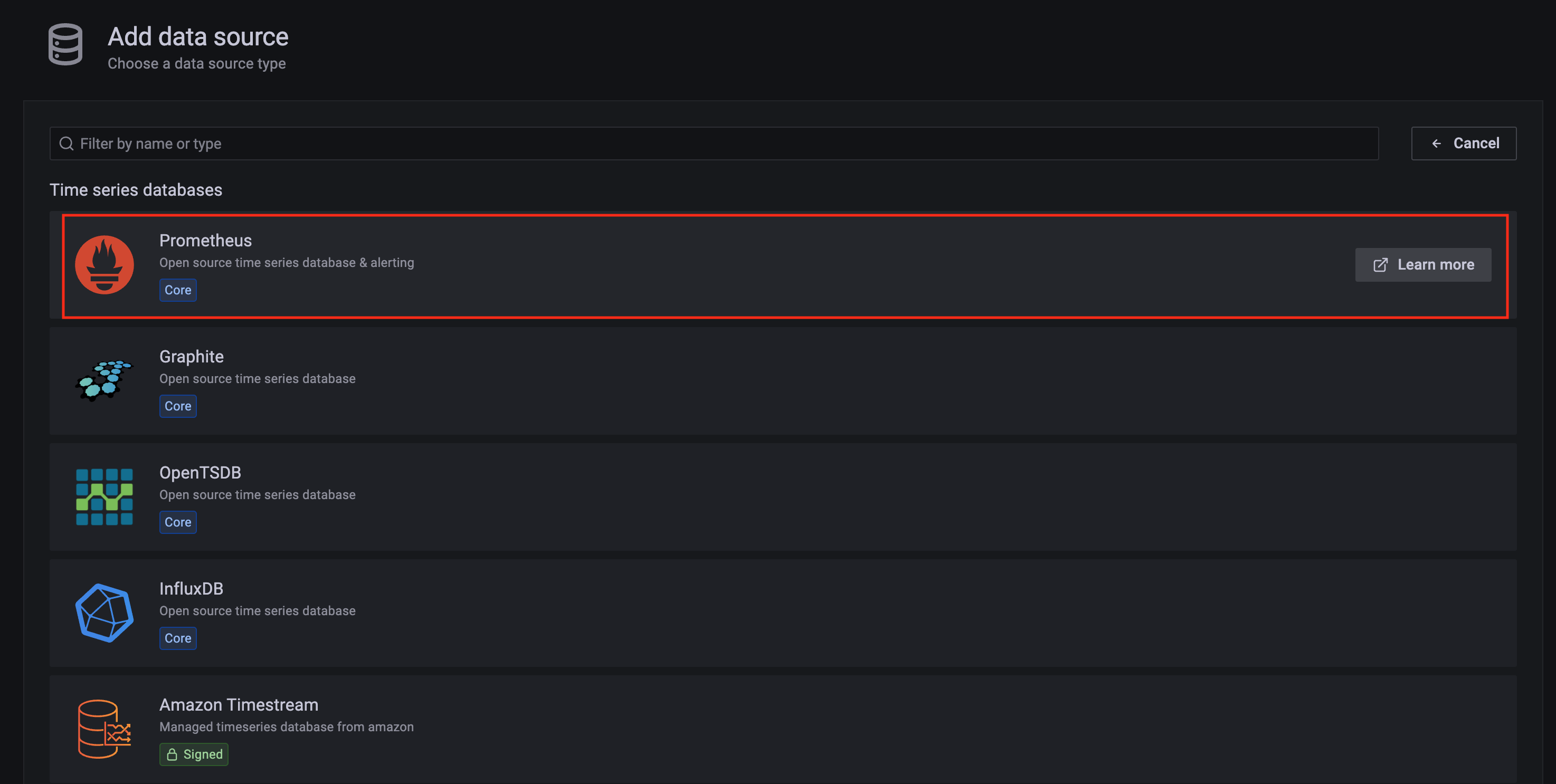
-
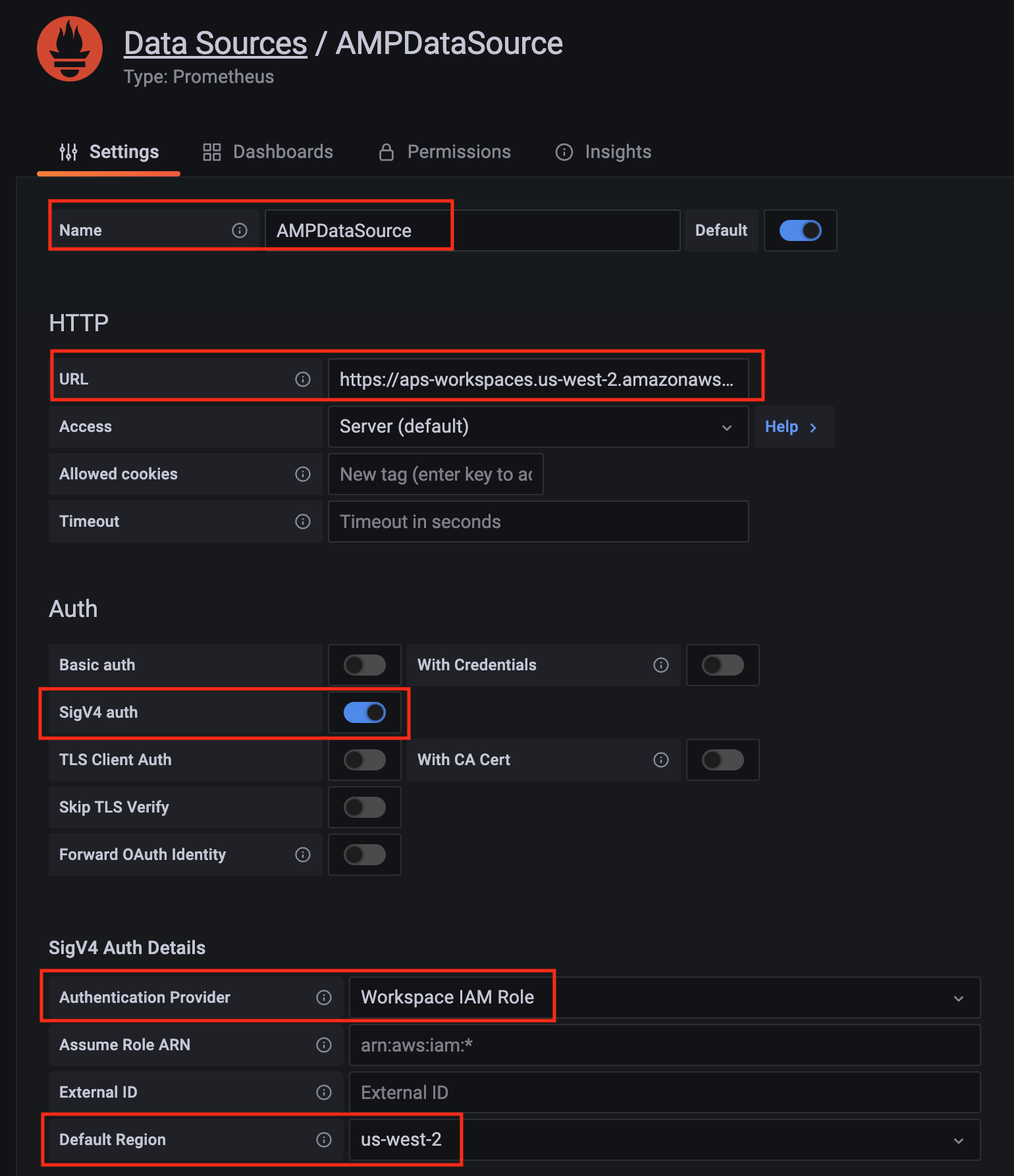
Configure Prometheus data source with the following details:
- Name:
AMPDataSource as an example.
- URL: add the AMP workspace remote write URL without the
api/v1/remote_write at the end.
- SigV4 auth: enable.
- Under the SigV4 Auth Details section:
- Authentication Provider: choose
Workspace IAM Role;
- Default Region: choose
us-west-2 (where you created the AMP workspace)
- Select the
Save and test, and a notification data source is working should be displayed.
-
Import a dashboard template by clicking on the plus (+) sign on the left navigation bar. In the Import screen, type 3119 in the Import via grafana.com textbox and select Import.
From the dropdown at the bottom, select AMPDataSource and select Import.
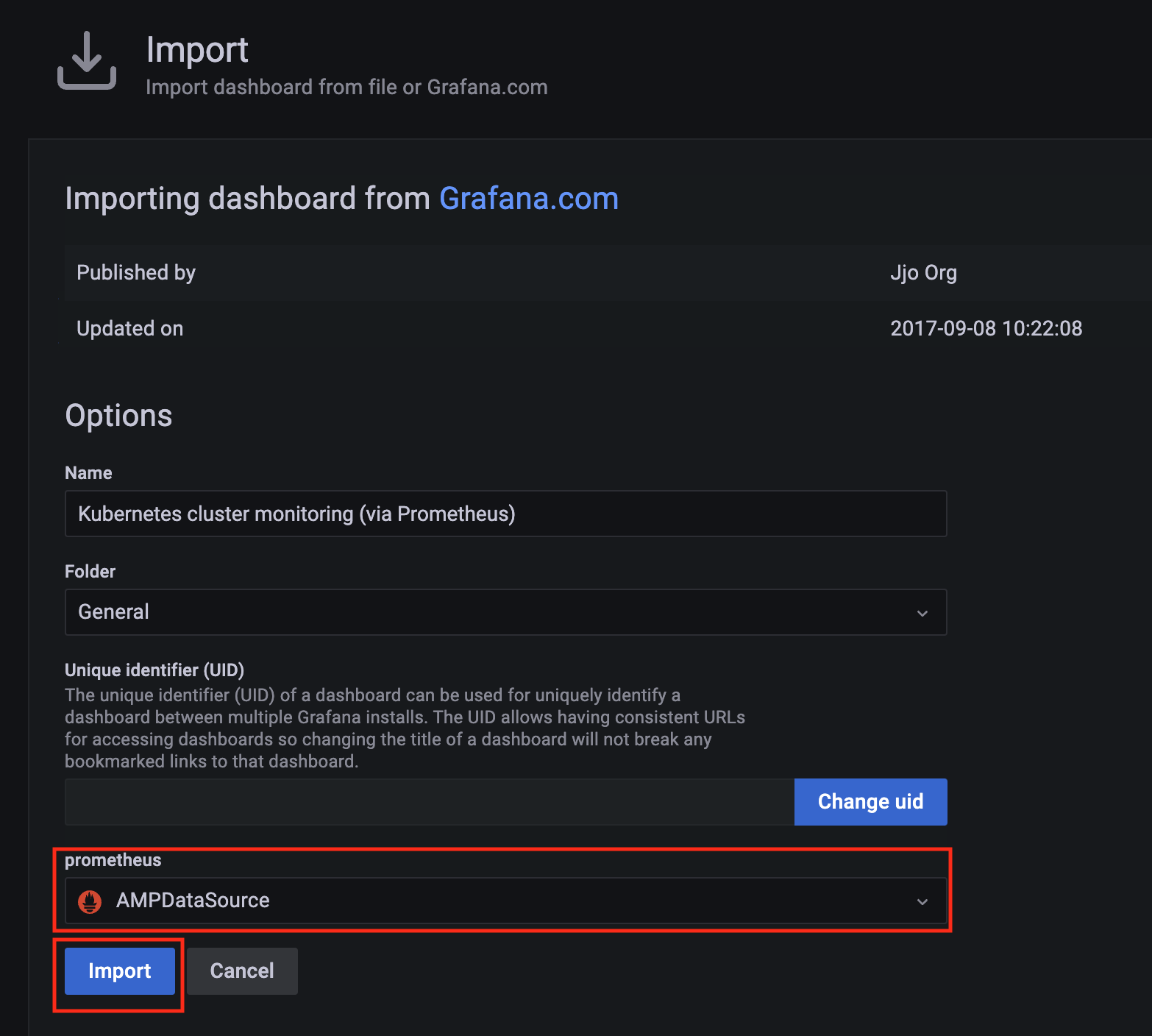
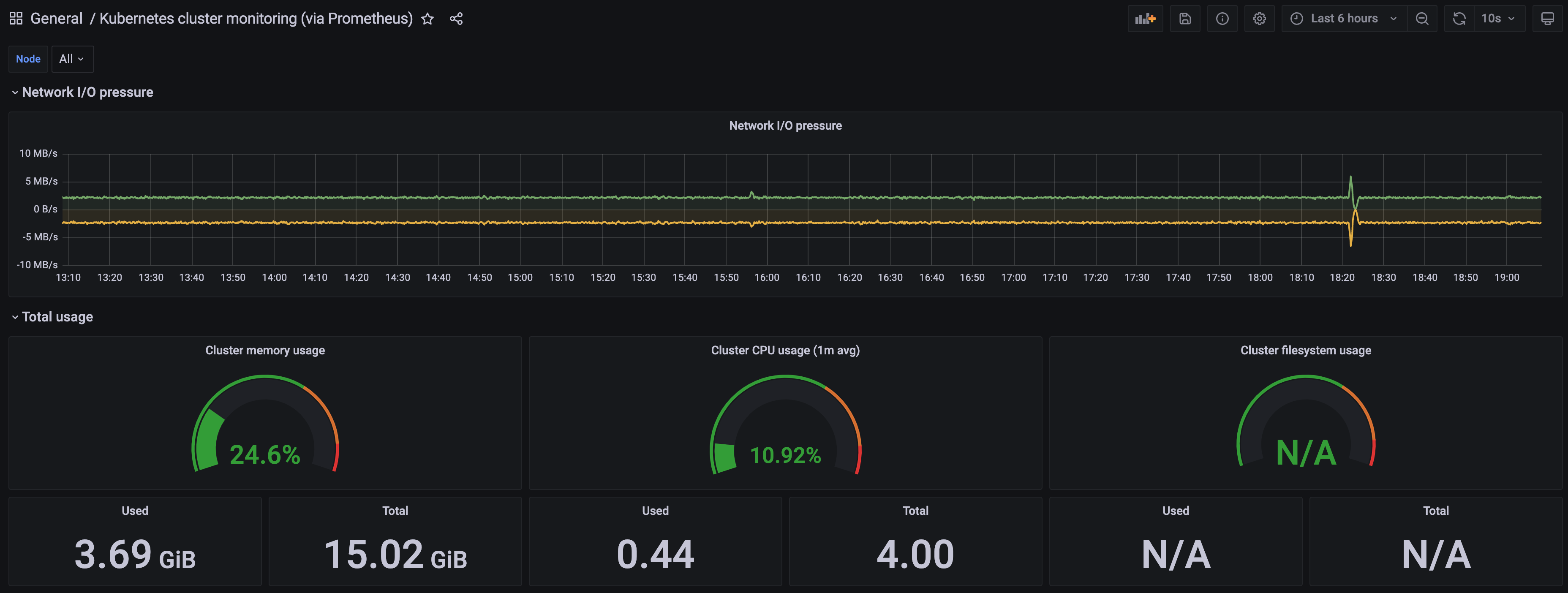
-
A Kubernetes cluster monitoring (via Prometheus) dashboard will be displayed.
2 - AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT)
Install/upgrade/uninstall ADOT
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package adot --cluster <cluster-name> > adot.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to adot.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file with daemonSet mode and default configuration:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Example package file with deployment mode and customized collector components to scrap
ADOT collector’s own metrics:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: deployment
replicaCount: 2
config:
receivers:
prometheus:
config:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: opentelemetry-collector
scrape_interval: 10s
static_configs:
- targets:
- ${MY_POD_IP}:8888
processors:
batch: {}
memory_limiter: null
exporters:
logging:
loglevel: debug
prometheusremotewrite:
endpoint: "<prometheus-remote-write-end-point>"
extensions:
health_check: {}
memory_ballast: {}
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [prometheus]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [logging, prometheusremotewrite]
telemetry:
metrics:
address: 0.0.0.0:8888
-
Create the namespace
(If overriding targetNamespace, change observability to the value of targetNamespace)
kubectl create namespace observability
-
Install adot
eksctl anywhere create packages -f adot.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
my-adot adot 19h installed 0.25.0-c26690f90d38811dbb0e3dad5aea77d1efa52c7b 0.25.0-c26690f90d38811dbb0e3dad5aea77d1efa52c7b (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update adot.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f adot.yaml
Upgrade
ADOT will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall ADOT, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> my-adot
3 - v0.21.1
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
4 - v0.23.0
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
5 - v0.25.0
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
6 - v0.39.0
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
7 - v0.41.1
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |









